o2 pure air duct cleaning

Emphysema is a disease of the lungs that usually develops after many years of smoking. Both chronic bronchitis and emphysema belong to a group of lung diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Once it develops, emphysema can’t be reversed. This is why not smoking or stopping smoking is very important. Emphysema is a condition that involves damage to the walls of the air sacs (alveoli) of the lung. Alveoli are small, thin-walled, very fragile air sacs located in clusters at the end of the bronchial tubes deep inside the lungs. There are about 300 million alveoli in normal lungs. As you breathe in air, the alveoli stretch, drawing oxygen in and transporting it to the blood. When you exhale, the alveoli shrink, forcing carbon dioxide out of the body. When emphysema develops, the alveoli and lung tissue are destroyed. With this damage, the alveoli cannot support the bronchial tubes. The tubes collapse and cause an “obstruction” (a blockage), which traps air inside the lungs.

Too much air trapped in the lungs can give some patients a barrel-chested appearance. Also, because there are fewer alveoli, less oxygen will be able to move into the bloodstream. Over 3 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with emphysema. Over 11 million Americans have COPD. Emphysema is most common in men between the ages of 50 and 70. Smoking is the number one factor. Because of this, emphysema is one of the most preventable types of respiratory diseases. Air pollutants in the home and workplace, genetic (inherited) factors (alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency), and respiratory infections can also play a role in causing emphysema. Cigarette smoking not only destroys lung tissue, it also irritates the airways. This causes inflammation and damage to cilia that line the bronchial tubes. This results in swollen airways, mucus production, and difficulty clearing the airways. All of these changes can lead to shortness of breath. Symptoms of emphysema may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and an increased production of mucus.

Often times, symptoms may not be noticed until 50% or more of the lung tissue has been destroyed. Until then, the only symptoms may be a gradual development of shortness of breath and tiredness (fatigue), which can be mistaken for other illnesses. People who develop emphysema have an increased risk of pneumonia, bronchitis, and other lung infections.
genie in room air purifierSee your doctor if any of these symptoms arise:
andrea air purifier uk The diagnosis of emphysema cannot be made solely on symptoms.
arlen ness stage 1 air cleaner coverSeveral tests are used to make the diagnosis. One simple test is to tap on your chest and listen with a stethoscope for a hollow sound. This means that air is being trapped in your lungs.
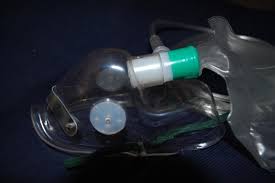
You might also talk to your doctor about whether testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is appropriate for you. Because emphysema can worsen over time and there is no known cure, treatment is focused on slowing the speed of decline. The type of treatment will depend on the severity of the disease. Quitting smoking: If you smoke, quit. This is the most important step you can take to protect your lungs. It is never too late to quit. Your doctor can help you find the best smoking quitting method for you. Bronchodilator medications: These medicines relax the muscles around the airways. They are often used to treat asthma. Bronchodilators, given through hand-held inhalants, produce more immediate results and have fewer side effects than oral medications. Anti-inflammatory medication: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways. However, long-term side effects of these drugs include osteoporosis, hypertension, high blood sugar, and fat redistribution. Oxygen therapy: Oxygen therapy is prescribed for patients whose lungs are not getting enough oxygen to the blood (hypoxemia).

These patients can’t absorb enough oxygen from the outside air and need to get more oxygen through a machine (a nasal catheter or a facemask). Lung volume reduction surgery: Lung volume reduction surgery involves removing a portion of diseased lung tissue, then joining together the remaining tissue. Doing this may relieve pressure on the breathing muscles and help improve lung elasticity (or stretch). The results of the surgery have been very promising. Not all patients with emphysema are candidates for this surgery. The best way to prevent or reduce further problems is to prevent respiratory infections by: © Copyright 1995-2016 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. This information is provided by the Cleveland Clinic and is not intended to replace the medical advice of your doctor or health care provider. Please consult your health care provider for advice about a specific medical condition. This document was last reviewed on: 1/28/2015…#9370Atmospheric air passes through the filter to remove the solid particles and dust by the help of air compressors.

Filters are placed on the suction side of the compressors where they are filtered and pressurized. By the developed pressure, water vapor changes to liquid water and removed by the separators. Water coolers decrease the temperature of the air, which have risen up due to compression. Turbo compressors operate in cascade and drive the clean air to Air Separation Unit at temperature of 45º C. The complete plant has three units The Air pre-cooling unit consists of the following equipment. This pre-cooling unit is also called as the air refrigeration system. The purpose of pre-cooling unit is to cool air from 45 º C to 10º C. The Air-H2O tower uses H2O coming from general circuit which is cooled down in the N2- H2O tower by means of refrigeration contained in the waste N2 coming from the cold box. A refrigeration unit in this water circuit brings additional refrigeration make-up, so that the temperature of H2O is brought down to 5 º C before the water enters the Air-water tower.

The air purification unit removes moisture, CO2 and hydrocarbons from pre-cooled compressed air by adsorbents present in the ducts and then air goes to main exchanger of the unit, through post filters where adsorbent final particles are removed. The Air purification unit consists of the following equipment. The pre-cooled compressed coming from Air-H2O tower enters into one of the driers which is in line while the other one is under regeneration. The driers consist of 2 bottles filled with activated alumina in the bottom and molecular sieves at the top, the air flow going from bottom to top. Moisture is adsorbed by Alumina, CO2 by molecular sieves. One of the two vessels is in operation, while the other is reactivated by waste N2 coming from the cold box. The total cycle is 10 hours with 10º C at the inlet of bottles, then the compressed air, dry and CO2 free, is filtered to eliminate dust particles it may carry by post filters and then enters the cold box. This unit mainly consists of the following equipment.

Purified air coming from the post-filters is sent directly to the main exchanger line. A part of the air is taken at an intermediate point of the exchangers and sent to centrifugal expansion turbines equipped with a brake generator to provide the necessary refrigeration to make-up for the thermal losses of the cold box. The adiabatic expansion drop the pressure down to approximately atmospheric pressure provides the main part of the refrigeration required by the plant. The other part is cooled in and sent to the bottom of the medium pressure column to perform the 1st separation. In this column, the up-flowing gas becomes enriched with N2 by contact with the down-coming liquid. This liquid result from the nitrogen condensation in the vaporizer / condenser located at the top of the column. From top to bottom, the medium pressure column gives the following products → Pure liquid N2 → Liquid with low O2 content used as reflux on the top of the low pressure column after passing through sub-cooler and expansion in a valve.

→ Rich liquid at the bottom, a liquid containing about 40% O2 sent to the low-pressure column, after passing through exchanger and expansion in a valve. The up flowing gas in the low pressure column is the gas vaporized in the vaporizer/ condenser is called main vaporizer and vaporizes liq.O2 at low pressure by condensation of medium pressure N2 in medium pressure column. The rich liquid sub-cooler makes it possible for the liquid oxygen to flow through filter by Thermo-siphon effect. This extra filtration permits to avoid abnormal accumulation of dangerous products in the O2 bath in case of accidental passage of impurities. The low pressure column gives → At the bottom, liquid O2 at a purity of 99.5 %. Part of this liquid O2 is sent directly at the outlet of the cold box for storage. The other part is vaporized in the air liquefier and then heated in the main exchanger line. → At the top, waste N2 which is heated in the main exchanger line. The pure N2 column is located above the low pressure column and gives at its top, pure N2 at 99.9 % purity, which is also heated in the main exchanger line.