ozein air purifier review
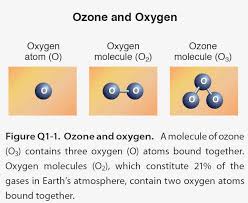
Email Page To a Friend Search for articles by the same authors or containing the same key words. Available online 5 July 2016In Press, Corrected Proof — Note to users Ozone has been used successfully for the treatment of various diseases for more than a decade. Its unique properties include immunostimulant, analgesic, antihypnotic, detoxicating, antimicrobial, bioenergetic and biosynthetic actions. Its atraumatic, painless, non invasive nature, and relative absence of discomfort and side effects increase the patient’s acceptability and compliance thus making it an ideal treatment choice specially for pediatric patients. This review is an attempt to highlight various treatment modalities of ozone therapy and its possible clinical applications in future.Ozone (O3) is a natural gaseous molecule made up of three oxygen atoms. The word ozone originates from the Greek word ozein, which means odor and was first used in 1840 by German chemist Christian Friedrich Schonbein “The father of ozone therapy.”

1 The stratosphere layer of the atmosphere contains abundance of ozone2 and it protects the living organisms from the ultraviolet rays. Ozone is heavier than air and hence it falls downward to earth from such high altitudes.3 It cleanses the air and combines with any pollutant that it comes in contact. This is earth’s natural way of self-cleansing.4Since more than 100 years medical grade ozone has been used as one of the non-medication methods of treatment. The first dentist to use ozone therapy in his practice was E.A. Fisch in the 1930’s, to aid in disinfection and wound healing during dental surgeries.5 The main use of ozone in dentistry relays on its antimicrobial properties.6Ozone therapy can be defined as a versatile bio-oxidative therapy in which oxygen/ozone is administered via gas or dissolved in water or oil base to obtain therapeutic benefits.7Three oxygen atoms constitute to form a tri-atomic molecule of ozone.
homedics® af-75 hypo allergenic hepa air cleaner reviews
Equal oxygen – oxygen bonds bound them together at an obtuse angle of 116 °C. The structure of ozone has an internal steric hindrance that prevents it from forming a triangular structure.8 As a result of this, instead of forming the expected double bonds each oxygen atom forms a single bond with the another oxygen atom resulting in a negative charge throughout the ozone molecule.2Ozone exists as colorless gas, with a pungent odor at room temperature, detectable even at concentrations as low as 0.02–0.05 ppm.9 Its half life varies with temperature variation.
honeywell hpa200 true hepa large room air purifier with allergen removerAt 20 °C it has a half-life of 40 min at 0 °C about 140 min.10Oxygen molecules in the air combines under the influence of factors such as ultraviolet radiation (from the sun) and electrical discharges (lightning).
rabbit air biogs 2.0 ultra quiet hepa air purifier
Intense physical stress on water (such as in areas of waterfalls and ocean waves crashing onto rocks) also results in production of ozone in nature.11 For medical use highly specific gazettes known as Ozone Generators are used for production of ozone. Medical grade oxygen is made to flow through high voltage tubes with outputs ranging from 4000 V to 14000 V. The Ozone Generators work on one of the three principles: Ultra-violet light lamp, Corona discharge or Cold plasma.12, 13 and 14 In dentistry, there are two widely used ozone units : the heal ozone15 and ozotop.11Ozone therapy has a wide range of applications in treating various diseases owing to its unique properties including antimicrobial, immunostimulant, analgesic, antihypnotic, detoxicating, bioenergetic and biosynthetic actions.Ozone causes inactivation of bacteria, viruses, fungi, yeast and protozoa. It disrupts the integrity of the bacterial cell envelope by oxidation of phospholipids and lipoproteins. Ozone at low concentration of 0.1 ppm, is sufficient to inactivate bacterial cells including their spores.16 In fungi, O3 inhibits cell growth at certain stages, budding cells being the most sensitive.17 With viruses, the O3 damages the viral capsid and upsets the reproductive cycle by disrupting the virus-to-cell contact with peroxidation.18Ozone therapy causes an increase in the red blood cell glycolysis rate.

This leads to the stimulation of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate leading to an increase in the amount of oxygen released to the tissues. Ozone activates the Krebs cycle by enhancing oxidative carboxylation of pyruvate, stimulating production of ATP. It also causes a significant reduction in NADH and helps to oxidize cytochrome C. There is stimulation of production of enzymes which act as free radical scavengers and cell-wall protectors: glutathione peroxidase, catalase and superoxide dismutase and prostacycline, a vasodilator.19Ozone administered at a concentration of between 30 and 55 μg/cc causes the greatest increase in the production of interferon and the greatest output of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-2 that launches an entire cascade of subsequent immunological reactions.20Ozone exposure induces a significant mean decrement in vital capacity. It significantly increases mean airway resistance and specific airway resistance but does not change dynamic or static pulmonary compliance or viscous or elastic work.

It also significantly reduces maximal transpulmonary pressure. And further more significantly increases respiratory rate and decreases tidal volume.20Ozone therapy presents great advantages when used as a support for conventional treatments and is indicated for use in a wide range of dental specialties.21Oral lesions are caused by various etiological factors; micro-organisms playing a major role for the same.22 Elimination of these microbial pathogens form the mainstay of an effective dental treatment. Various bacteria have been studied in relation to ozone treatment. It has been reported that an exposure of about 60 s exhibited 99.9% killing efficiency against cariogenic bacteria such as Actinomyces naeslundii, Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus casei. However, exposure for such a long period showed degradation of salivary proteins and hence 10 s–30 s of exposure was proven to be effective in killing a significant number of bacteria. Considering the medium for the survival rates of S. mutans and L. casei the salivary medium depicted greater survival than the saline medium.